Abstract
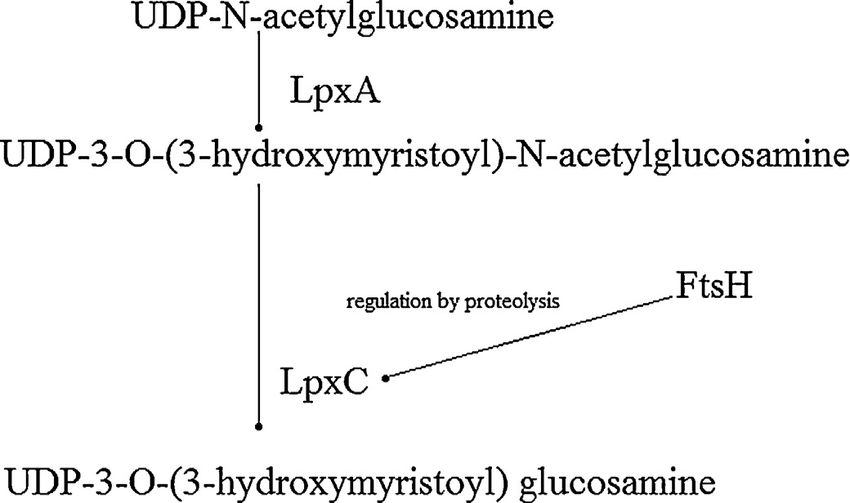
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is an essential structural component found in Gram-negative bacteria. The molecule is comprised of a highly conserved lipid A and a variable outer core consisting of various sugars. LPS plays important roles in membrane stability in the bacterial cell and is also a potent activator of the human immune system. Despite its obvious importance, little is understood regarding the regulation of the individual enzymes involved or the pathway as a whole. LpxA and LpxC catalyze the first two steps in the LPS pathway. The reaction catalyzed by LpxA possesses a highly unfavourable equilibrium constant with no evidence of coupling to an energetically favourable reaction. In our model the presence of the second enzyme LpxC was sufficient to abate this unfavourable reaction and confirming previous studies suggesting that this reaction is the first committed step in LPS synthesis. It is believed that the protease FtsH regulates LpxC activity via cleavage. It is also suspected that the activity of FtsH is regulated by a metabolite produced by the LPS pathway; however, it is not known which one. In order to investigate these mechanisms, we obtained kinetic parameters from literature and developed estimates for other simulation parameters. Our simulations suggest that under modest increases in LpxC activity, FtsH is able to regulate the rate of product formation. However, under extreme increases in LpxC activities such as over-expression or asymmetrical cell division then FtsH activation may not be sufficient to regulate this first stage of synthesis.